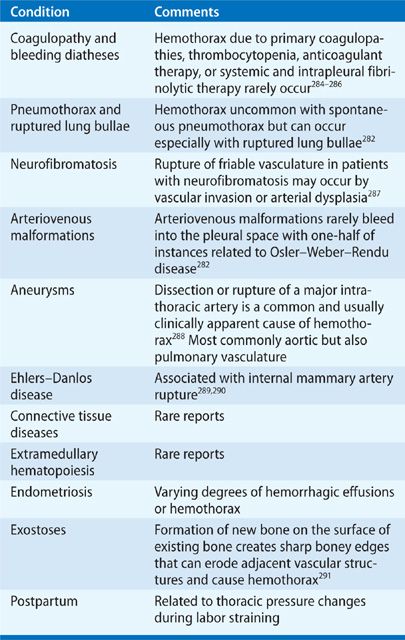
what is the prognosis for malignant pleural effusion
This can cause you to feel short of breath andor have chest discomfort. The prognosis of the patient with a pleural effusion depends on the underlying condition.

Overall Survival Probability According To Malignant Pleural Effusion Download Scientific Diagram
Malignant pleural effusions MPE develop as a direct extension of cancer into the pleural space or they are due to inflammation induced by malignancy.
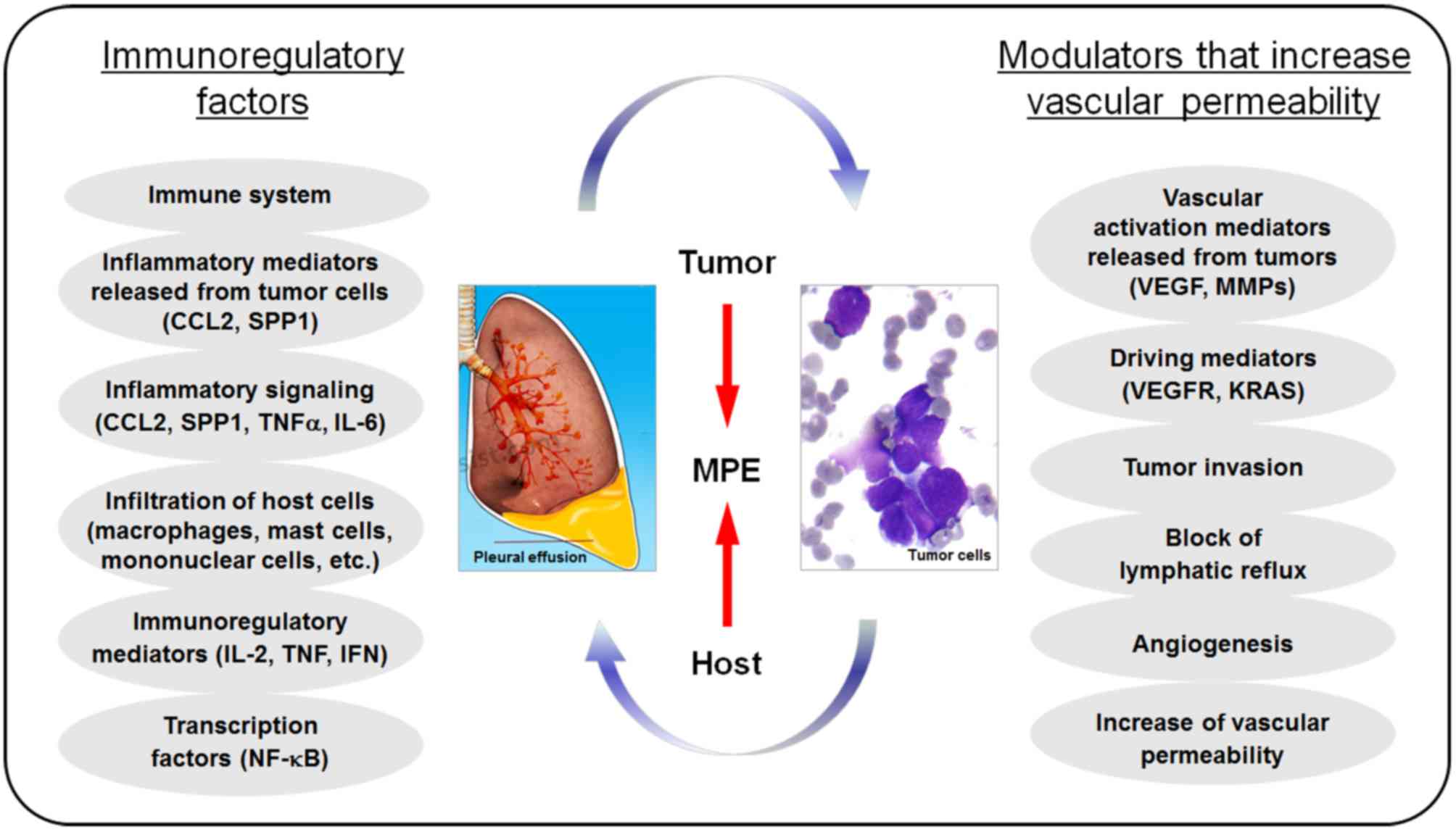
. This condition is associated with very high mortality with life expectancy ranging from 3 to 12 months. The aim of MPE therapeutic approaches should be effective treatment and a short hospital stay. Patients with pleural effusion and ovarian cancer had the best median survival 21 months compared with those with other primary tumors.
Median survival in these patients ranges from 3 to 12 months with the shortest survival period presenting in lung cancer patients. 18 19 The most common associated. Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key.
The pleural effusion is usually caused by a disturbance of the normal Starling forces regulating reabsorption of fluid in the pleural space secondary to obstruction of mediastinal lymph nodes draining the parietal pleura. However most patients with a pleural effusion have no long-term sequelae. Median survival after diagnosis is 4 to 9 months 13 although prognosis varies considerably depending on the type and stage of the malignancy.
Symptomatic malignant pleural effusion is a common clinical problem. It represents disseminated disease and confers a poor prognosis. Malignant Pleural Effusion A malignant pleural effusion MPE is the build up of fluid and cancer cells that collects between the chest wall and the lung.
The diagnosis of MPE can be established by the presence of malignant cells in the pleural fluid or tissue. Malignant pleural effusion MPE is a common clinical problem that results in disabling breathlessness for patients with advanced malignancy. A number of factors may help predict survival of patients with malignant pleural disease including tumour characteristics extent of disease comorbidities and the composition of the effusion.
Development of a malignant pleural effusion is associated with a very poor prognosis with median survival of 4 months and mean survival of less than 1 year. Median overall survival was 9 months. Roughly 150000 malignant pleural effusions MPE are diagnosed in the United States each year.
How patients are best managed depends on clinical circumstances. Development of a malignant pleural effusion is associated with a very poor prognosis with median survival of 4 months and mean survival of less than 1 year. Despite progress in therapeutic options the prognosis remains severe and the average survival is 4-9 months from the diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion.
The prognosis of cases where the effusion is due to carcinoma of the lung or due to cancer of the. Malignant pleural effusion survival prognostication in an Asian population The LENT modified-LENT and PROMISE scores have poor accuracy of survival prognostication in Asian patients with MPE undergoing pleuroscopy. A malignant pleural effusion is often first suspected because of symptoms or findings on a chest X-ray or CT scan.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med Vol. If due to heart failure cirrhosis or malignancy the effusion is likely to recur. The medial survival of patients with breast cancer was 6 months and those with either lung cancer or lymphoma had a median survival of 4 months Tables 3 and 4.
Development of a malignant pleural effusion is associated with a very poor prognosis with median survival of 4 months and. Palliation of symptoms has been the goal for the management of these effusions while keeping the patients hospital stay to a minimum. 58 in addition inflammation-based scoring systems have been associated with overall prognosis in a number of cancer types including mesothelioma.
Certain types of cancer. Studies are contributing evidence on an increasing number of therapeutic options therapeutic thoracentesis thoracoscopic pleurodesis or thoracic drainage indwelling pleural catheter. The proposed SELECT prognostication model is accurate at identifying patients with high probability of survival at 90 days.
The majority of cases are caused by lung and breast cancer and since MPE represents advanced disease the prognosis is generally poor. Breast cancer is the second most common cause of MPE. A non-concurrent cohort study was carried out in which 120 evaluable patients with malignant pleural effusion underwent pleurodesis.
Patients in these stages often have a poor prognosis with an average life expectancy of less than six months. Sometimes a pleural effusion can occur as a result of inflammation lung obstruction trauma or another medical condition that may not be due to cancer. M anaging patients with malignant pleural effusion can be challenging.
It is a fairly common complication in a number of different cancers. MPEs are most commonly secondary to lung cancer with adenocarcinoma type most frequently associated with the development of pleural effusion. If your doctor suspects a malignant pleural effusion the next step is usually a thoracentesis a procedure in which a needle is inserted through the chest wall into the pleural space to get a sample of the fluidThis fluid is then examined under a.
Moreover mortality is higher for patients with malignant pleural effusion compared with those with metastatic cancer but no malignant pleural effusion. Symptoms are often distressing and its presence signifies advanced disease. Clinical data and pleural fluid parameters were analysed.
Lung 40 breast 266 and unknown primary site 125 carcinomas were the most frequent neoplasms. For people with cancer pleural effusions are often malignant see above. Malignant pleural effusion MPE occurs in 15 of all cancer patients and usually portends poor prognosis while also serving to limit the patients quality of life.
Prognosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion As previously mentioned this condition often indicates the presence of advanced stage lung cancer or breast cancer. This means that there are cancer cells in the pleural space causing fluid to build up. The removal of a large volume of pleural fluid could rapidly expand atelectatic lung regions.
Malignant effusions may change the staging and subsequent prognosis of the underlying cancer. The prognosis of cases where the effusion is due to carcinoma of the lung or due to cancer of the. The average malignant pleural effusion life expectancy is a little less than six months with the median survival time being as less as four months.
Sadly the average life expectancy for lung cancer with a malignant pleural effusion is less than six months. The median survival time the time at which 50 percent of people will have died is four months though some people survive longer.
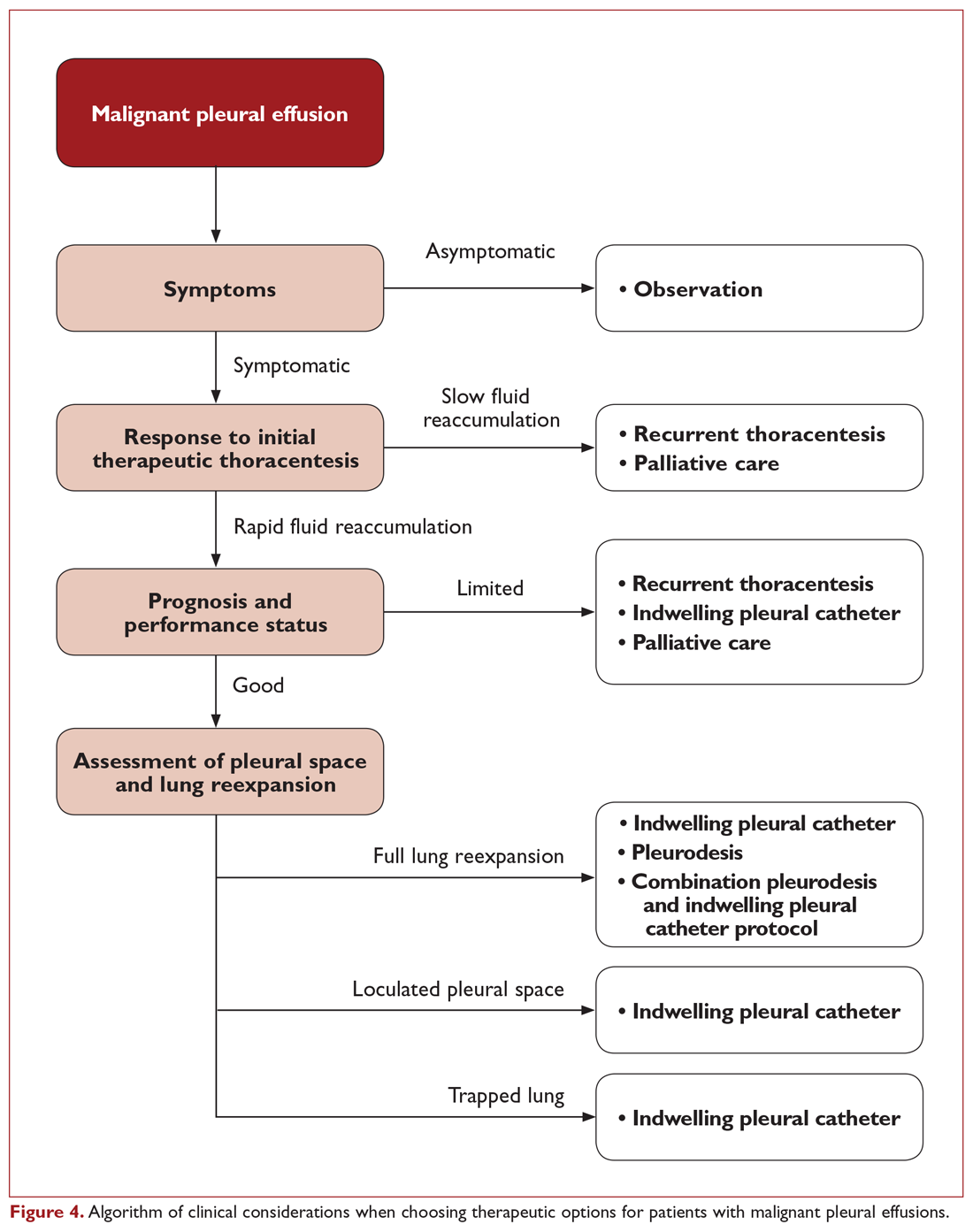
Malignant Pleural Effusion Therapeutic Options And Strategies Pulmonary Health Hub

Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key
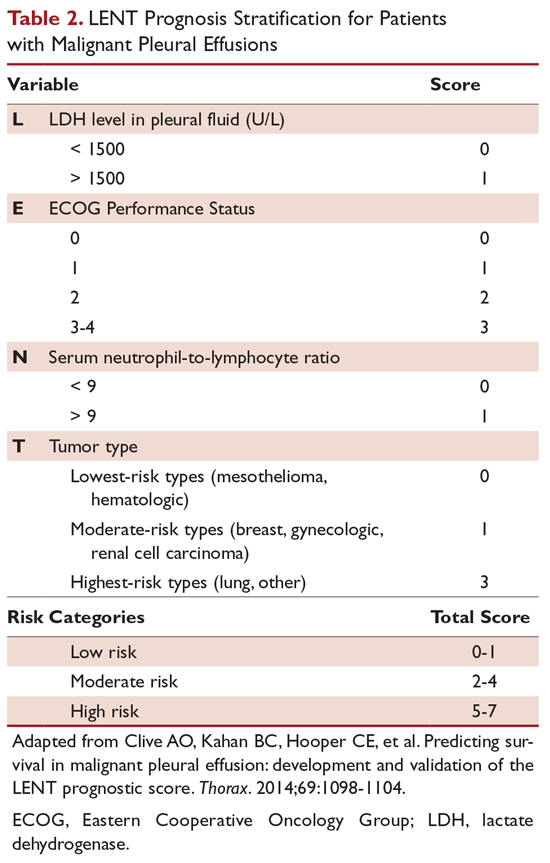
Malignant Pleural Effusion Evaluation And Diagnosis Pulmonary Health Hub

Ers Eacts Statement On The Management Of Malignant Pleural Effusions European Respiratory Society

Pdf Malignant Pleural Effusion Medical Approaches For Diagnosis And Management Semantic Scholar

The Role Of Vegf In The Diagnosis And Treatment Of Malignant Pleural Effusion In Patients With Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Review

Malignant Pleural Effusion Management Keeping The Flood Gates Shut The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Prognostic Factors For Survival After Surgical Palliation Of Malignant Pleural Effusion Journal Of Thoracic Oncology
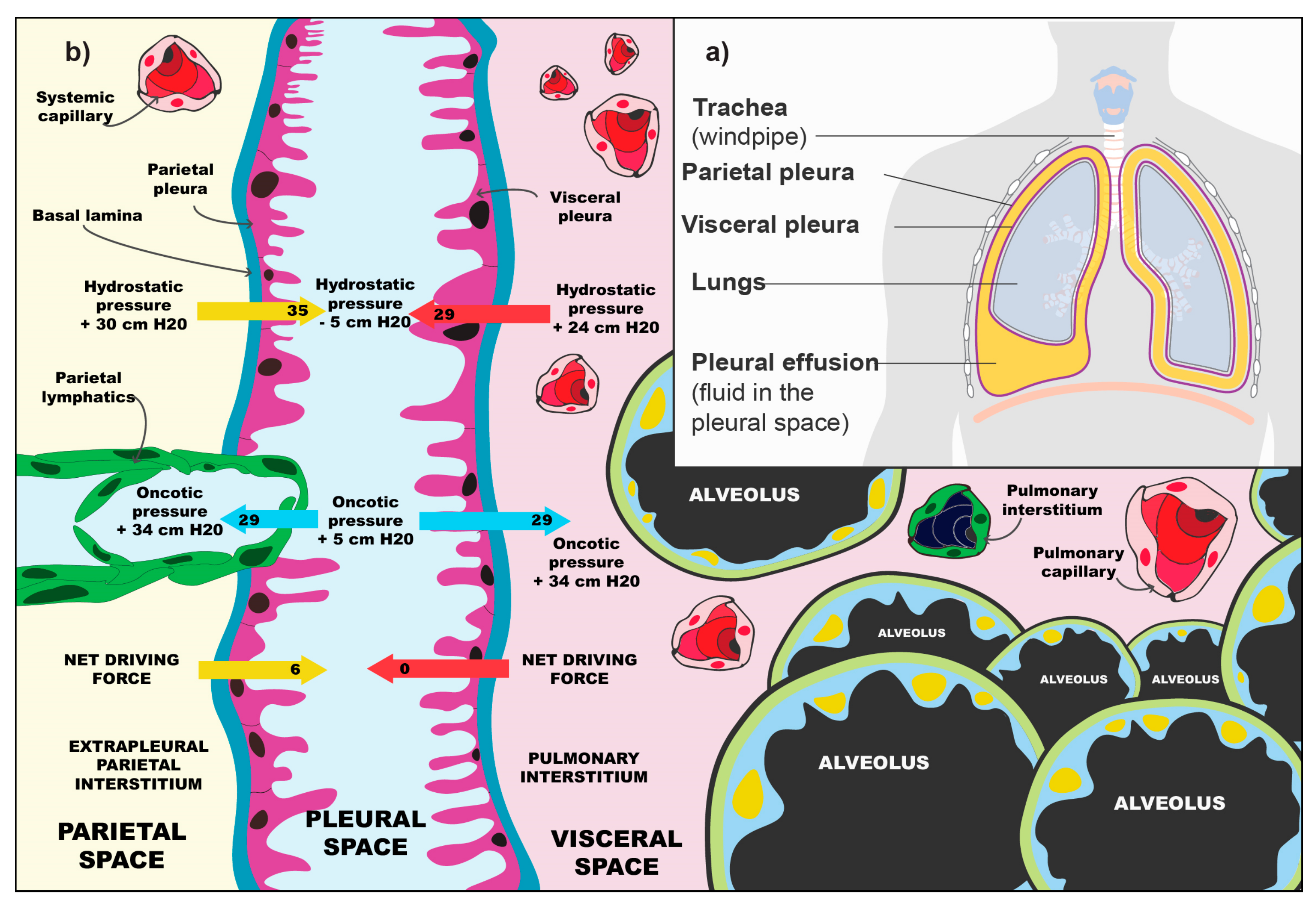
Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html

Treatment Options For Malignant Pleural Effusions Download Table
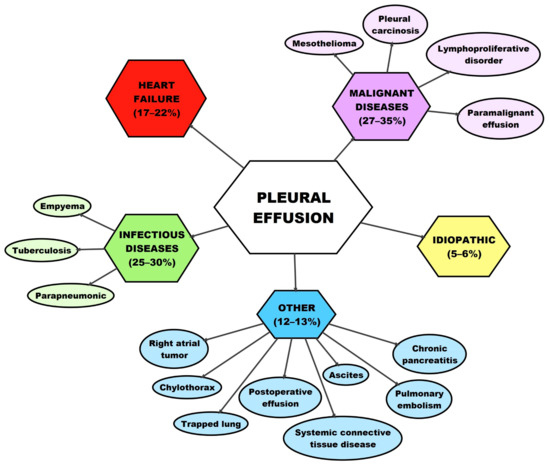
Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html
Malignant Pleural Effusion Still A Long Way To Go Researcher An

The Diagnostic Steps In Suspected Malignant Pleural Effusion Table 1 Download Scientific Diagram

Prognostic Impact Of Malignant Pleural Effusion At Presentation In Patients With Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

Malignant Pleural Effusion 03102017 Youtube

Management Of Malignant Pleural Effusions The Figure Is Modified From Download Scientific Diagram

Prognostic Factors For Survival After Surgical Palliation Of Malignant Pleural Effusion Journal Of Thoracic Oncology
The Current Aetiology Of Malignant Pleural Effusion In The Western Cape Province South Africa